Sustainability
Facts and figures
Act now
Companies
NGOS
Products
Sustainability
The definition of sustainability

3 pillars of sustainability
The concept of sustainability is often divided into three pillars:
- Environment
- Social
- Economic
Informally, these are profits, the planet and people.
Environmental sustainability
This concept places more emphasis on the life-support systems, such as the atmosphere or the soil. These must be preserved for economic production or human life to take place at all.
Social sustainability
In contrast, it focuses on the human impact of economic systems. This includes attempts to eradicate poverty and hunger and combat inequality.
Economic sustainability
This looks at the conservation of the natural resources that provide the physical inputs for economic production, including renewable and exhaustible inputs.

The United Nations 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The centerpieces of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development are the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which represent an urgent call to action by all countries – developed and developing – as part of a global partnership.
In doing so, the participating countries recognize that the eradication of poverty and other deprivations must go hand in hand with strategies to improve health and education, reduce inequality and boost economic growth. This is all done while combating climate change and working to protect our oceans and forests.
The ecological footprint
What is an ecological footprint?

Causes and reasons for different ecological footprints
The different lifestyles and consumption patterns result in large differences in the ecological footprints between countries or population groups.
The quantities of food consumed, the use of goods and services and the CO2 emissions generated during the provision of goods and services are important influencing factors here.


Source of Illustration: WWF Japan and Global Footprint Network; Ecological Footprint for Sustainable Living in Japan
Earth Overshoot Day
The Earth Overshoot Day marks the date when humanity’s demand for ecological resources and services in a given year exceeds what Earth can regenerate in that year.
On Earth Overshoot Day, we humans have used up all the natural resources that the earth can regenerate and sustainably provide within a year. With the steady increase in the consumption of global resources, this day falls on an earlier date each year.
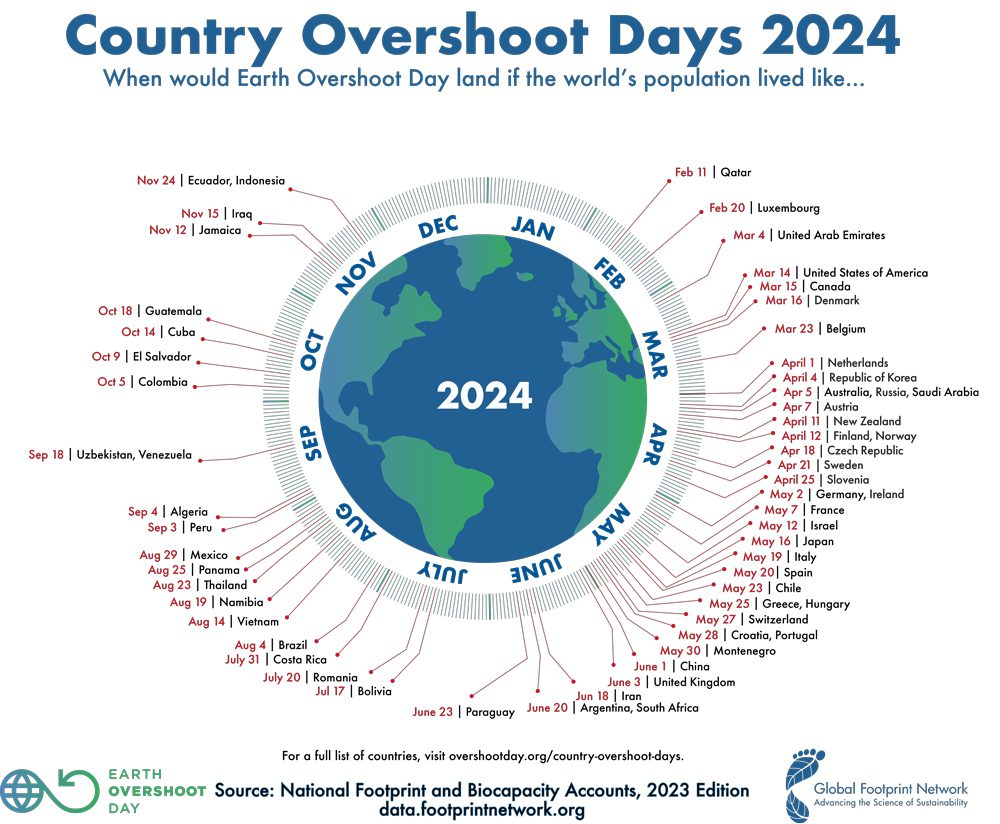
You too can change your environmental footprint with your own behaviour when shopping, eating and travelling.
Carbon handprint
What is a carbon handprint?

What is a carbon handprint and how does it differ from a carbon footprint?
The carbon handprint measures the positive impact of a product on the environment, while a carbon footprint measures the negative impact (absolute greenhouse gas emissions) of a product on the environment.

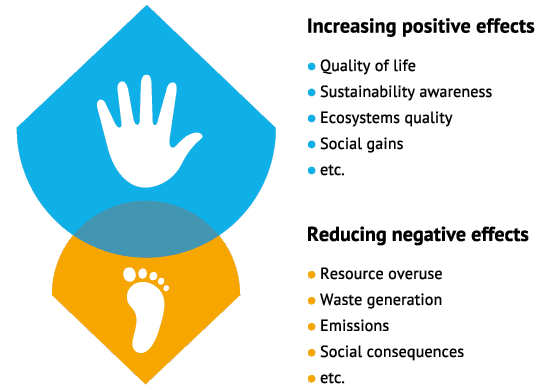
Source: Handprint – CSCP gGmbH

Greenuniverse
The sustainability experts – we clear the way for you in the sustainability jungle.
Sustainability is in our DNA. We are happy to share our passion and many years of experience with you.
Issues
Nourishment
Sustainability
contact
Gaertnerstrasse 11, CH-4656 Starrkirch-Wil, Switzerland
(+41) 79 756 31 89